Fast, Simple and Accurate
Data Unit Converter
Welcome to DataUnitConverter.com – Your One-Stop Destination for Effortless Digital Data Size and Transfer Rate Conversions!
Table of Contents
- What is Digital Data?
- How Digital Data is measured?
- What is Data Unit Conversion?
- Digital Data Storage Measurement Units in Order : Smallest to Largest
-
Comparison between Decimal (SI Standard) and Binary (IEC Standard) units
- Decimal and Binary Bit Units
- Decimal and Binary Byte Units
- Relationship between different Data Measurement Units
- Digital Data Units - Complete List and Definitions
What is Digital Data?
Digital data refers to information that is stored and processed in a digital format, typically represented as binary code, which consists of combinations of the digits 0 and 1. This binary code is the fundamental language of computers and digital devices.
In digital form, data can represent various types of information, such as text, numbers, images, audio, and video. Each piece of data is broken down into discrete units called bits, and a collection of bits forms bytes. The arrangement and interpretation of these bits determine the meaning of the data.
Digital data can be easily manipulated, transmitted, and stored by electronic devices, making it a central aspect of modern computing and communication systems. Examples of digital data sources include documents stored on a computer, photos taken with a digital camera, music files, and videos streamed online. The opposite of digital data is analog data, which is represented in a continuous, non-discrete form.
How Digital Data is measured?
Digital data is measured in terms of bits and bytes. Bit,Nibble and Byte are the fundamental digital data units. The larger units, multiples of bits and bytes, are further categorized as Binary and Decimal units.
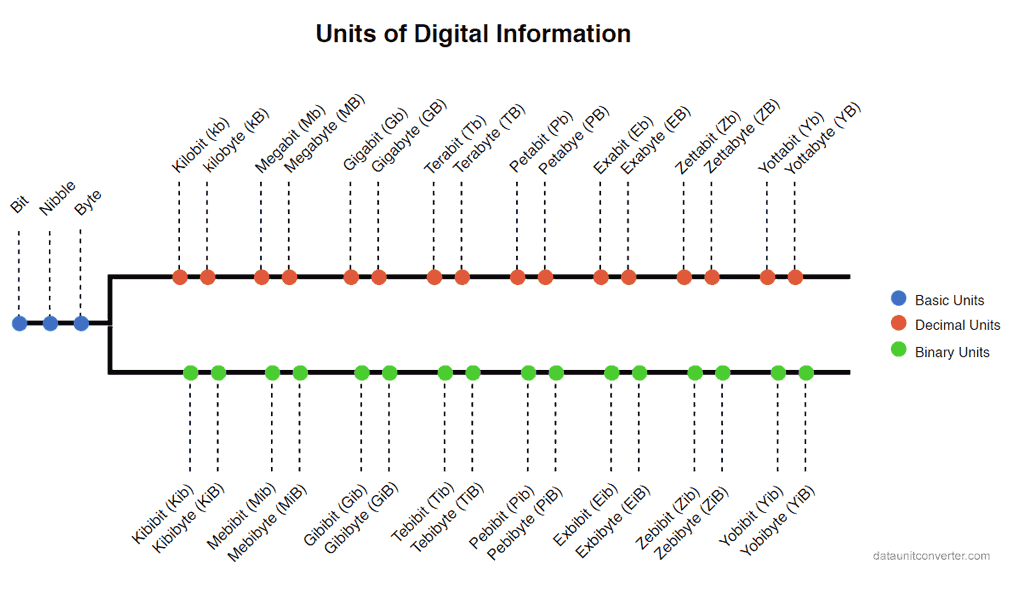
Decimal units are defined by SI(International System of Units), use Metric prefixes such as kilo, mega etc. Decimal units are multiples of 1000.
Binary units are comparatively newer, defined by IEC(International Electro technical Commission), prefixed with kibi, mebi etc. evaluated as multiples of 1024. You can find further details on each units below.
Regional differences on the Data Unit usage
Regional differences in data unit usage can vary based on factors such as historical conventions, regulatory frameworks, and technological advancements. Here is an overview of data unit usage in the United States, the United Kingdom, and the rest of the world.
United States (US)
In the United States, the most commonly used data unit is the gigabyte (GB), which is often used to measure storage capacity for digital devices like smartphones, computers, and hard drives. Internet service providers typically advertise their broadband plans in terms of download and upload speeds, usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). However, when it comes to tracking data usage, internet service providers and mobile carriers often refer to data consumption in terms of gigabytes or terabytes (TB). For example, mobile data plans may offer a certain amount of data per month, such as 5GB or 10GB.
United Kingdom (UK)
The United Kingdom generally follows similar data unit usage patterns as the United States. The gigabyte (GB) is the most common unit for measuring storage capacity and data usage. Internet service providers in the UK also advertise their broadband plans in terms of download and upload speeds, usually in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). Mobile data plans in the UK are typically measured in gigabytes (GB) as well.
Rest of the world
In the rest of the world, including countries outside the US and UK, data unit usage can vary to some extent. The International System of Units (SI) recommends using base-10 prefixes for decimal multiples of a unit. However, historically, binary prefixes have been used in the context of data storage and data transmission. For instance, the binary prefix "gibi" (Gi) represents 2^30 (1,073,741,824) bytes, while the decimal prefix "giga" (GB) represents 10^9 (1,000,000,000) bytes.
It's important to note that there can be some variations and regional preferences in data units, especially when it comes to data transfer rates, where units like kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), and gigabits per second (Gbps) are commonly used. Nonetheless, the fundamental data units remain the same.
What is Data Unit Conversion?
Data unit conversion refers to the process of converting one unit of data to another unit of data. It is a common task in computer science and information technology, where different data units are used to measure the amount of data stored or transmitted. Some common data units include bits, bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, and terabytes.
Converting data units can be useful for a variety of purposes, such as estimating file sizes, measuring network speeds, and optimizing data storage. The process of conversion involves multiplying or dividing the value of the original data unit by a conversion factor, which is based on the relationship between the two units being converted.
Understanding how to convert data units is an essential skill in computer science and information technology, and can be learned through practice and familiarity with common conversion factors.
At dataunitconverter.com, you can access a wide range of tools to convert between different data storage and transfer units. Additionally, it offers a convenient Conversion Table Generator, allowing you to convert a list/range of values from one data unit to another.
Digital Data Storage Measurement Units in Order : Smallest to Largest
Bit (b) is the smallest unit to measure digital data, whereas Byte is commonly used as the smallest addressable unit of storage in many computer systems. A Nibble can be formed by grouping 4 bits, can have up to 16 values.
| Bit (b) 0 or 1 (Basic Unit) |
Nibble 1 Nibble = 4 Bits |
Byte (B) 1 Byte = 8 Bits |
| Bit Units | Byte Units |
| Kilobit (kbit) 1 Kilobit = 103 or 1000 Bits | Kilobyte (kB) 1 Kilobyte = 103 or 1000 Bytes |
| Megabit (Mbit) 1 Megabit = 106 or 10002 Bits | Megabyte (MB) 1 Megabyte = 106 or 10002 Bytes |
| Gigabit (Gbit) 1 Gigabit = 109 or 10003 Bits | Gigabyte (GB) 1 Gigabyte = 109 or 10003 Bytes |
| Terabit (Tbit) 1 Terabit = 1012 or 10004 Bits | Terabyte (TB) 1 Terabyte = 1012 or 10004 Bytes |
| Petabit (Pbit) 1 Petabit = 1015 or 10005 Bits | Petabyte (PB) 1 Petabyte = 1015 or 10005 Bytes |
| Exabit (Ebit) 1 Exabit = 1018 or 10006 Bits | Exabyte (EB) 1 Exabyte = 1018 or 10006 Bytes |
| Zettabit (Zbit) 1 Zettabit = 1021 or 10007 Bits | Zettabyte (ZB) 1 Zettabyte = 1021 or 10007 Bytes |
| Yottabit (Ybit) 1 Yottabit = 1024 or 10008 Bits | Yottabyte (YB) 1 Yottabyte = 1024 or 10008 Bytes |
| Bit Units | Byte Units |
| Kibibit (Kibit) 1 Kibibit = 210 or 1024 Bits | Kibibyte (KiB) 1 Kibibyte = 210 or 1024 Bytes |
| Mebibit (Mibit) 1 Mebibit = 220 or 10242 Bits | Mebibyte (MiB) 1 Mebibyte = 220 or 10242 Bytes |
| Gibibit (Gibit) 1 Gibibit = 230 or 10243 Bits | Gibibyte (GiB) 1 Gibibyte = 230 or 10243 Bytes |
| Tebibit (Tibit) 1 Tebibit = 240 or 10244 Bits | Tebibyte (TiB) 1 Tebibyte = 240 or 10244 Bytes |
| Pebibit (Pibit) 1 Pebibit = 250 or 10245 Bits | Pebibyte (PiB) 1 Pebibyte = 250 or 10245 Bytes |
| Exbibit (Eibit) 1 Exbibit = 260 or 10246 Bits | Exbibyte (EiB) 1 Exbibyte = 260 or 10246 Bytes |
| Zebibit (Zibit) 1 Zebibit = 270 or 10247 Bits | Zebibyte (ZiB) 1 Zebibyte = 270 or 10247 Bytes |
| Yobibit (Yibit) 1 Yobibit = 280 or 10248 Bits | Yobibyte (YiB) 1 Yobibyte = 280 or 10248 Bytes |
Comparison between Decimal (SI Standard) and Binary (IEC Standard) units.
Bit Units
| Decimal Unit | Equivalent in Bits | Binary Unit | Equivalent in Bits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kilobit | 1,000 | Kibibit | 1,024 |
| Megabit | 1,000,000 | Mebibit | 1,048,576 |
| Gigabit | 1,000,000,000 | Gibibit | 1,073,741,824 |
| Terabit | 1,000,000,000,000 | Tebibit | 1,099,511,627,776 |
| Petabit | 1,000,000,000,000,000 | Pebibit | 1,125,899,906,842,624 |
| Exabit | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 | Exbibit | 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 |
| Zettabit | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | Zebibit | 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 |
| Yottabit | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | Yobibit | 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 |
Byte Units
| Decimal Unit | Equivalent in Bytes | Binary Unit | Equivalent in Bytes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kilobyte | 1,000 | Kibibyte | 1,024 |
| Megabyte | 1,000,000 | Mebibyte | 1,048,576 |
| Gigabyte | 1,000,000,000 | Gibibyte | 1,073,741,824 |
| Terabyte | 1,000,000,000,000 | Tebibyte | 1,099,511,627,776 |
| Petabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000 | Pebibyte | 1,125,899,906,842,624 |
| Exabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 | Exbibyte | 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 |
| Zettabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | Zebibyte | 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 |
| Yottabyte | 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 | Yobibyte | 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 |
Relationship between different Data Measurement Units
Following are the popular Digital Data Units defined by International Electro technical Commission(IEC) and International System of Units(SI). All the conversion logic used in this website align with these standards.
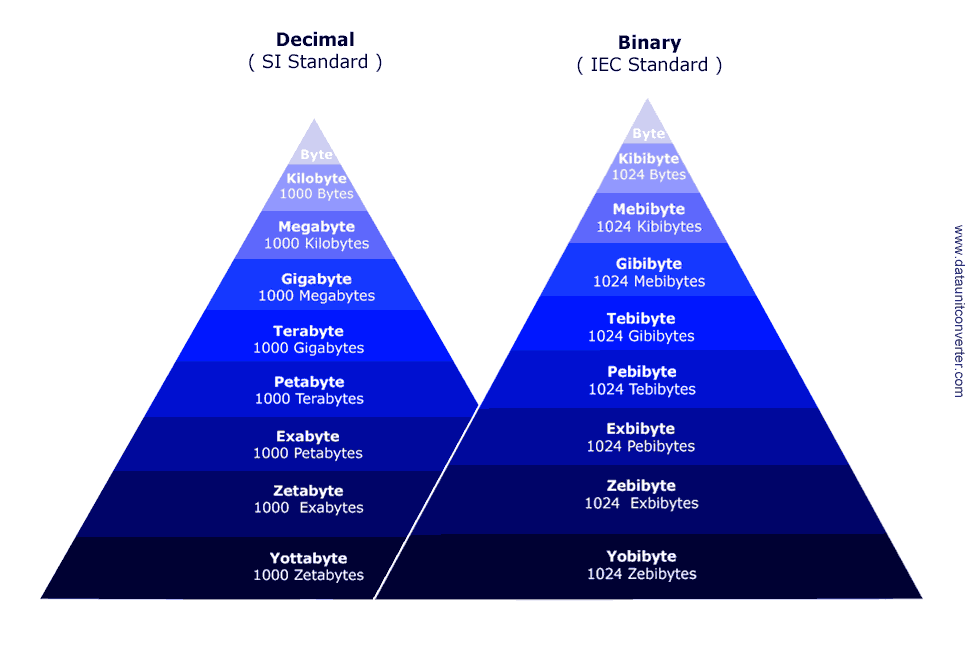
Each Decimal unit (kb, kB, Mb, MB, Gb, GB, Tb, TB, Pb, PB, Eb, EB, Zb, ZB, Yb, YB) is 1000 times larger than its preceding unit, whereas each Binary unit(Kibit, KiB, Mibit, MiB, Gibit, GiB, Tibit, TiB, Pibit, PiB, Eibit, EiB, Zibit, ZiB, Yibit, YiB) is 1024 times larger than the preceding unit. Below table represents how these units are related to each other.
Digital Data Units - Complete List and Definitions
A Bit (short for 'binary digit') is the basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. It is a binary value, meaning it can have one of two values=> 0 or 1. Bits are used to represent data in computers and other electronic devices. They are the building blocks of digital information, and are used to store, transmit, and process data.
A Nibble is a unit of digital information that consists of 4 bits. It is half of a byte and can represent a single hexadecimal digit. It is used in computer memory and data storage and sometimes used as a basic unit of data transfer in certain computer architectures.
A Byte is a unit of digital information that typically consists of 8 bits and can represent a wide range of values such as characters, binary data and it is widely used in the digital world to measure the data size and data transfer speed.
A Kilobit (kb or kbit) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1000 bits. It is commonly used to express data transfer speeds, such as the speed of an internet connection and to measure the size of a file. In the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of Kibibit (Kibit) is used instead.
A Kibibit (Kib or Kibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1024 bits. It is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC) and is used to measure the amount of digital data. The prefix 'kibi' is derived from the binary number system, it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'kilobit' (Kb) and it is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Kilobyte (kB) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1000 bytes (or 8,000 bits) and commonly used to express the size of a file or the amount of memory used by a program. It is also used to express data transfer speeds and in the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of kibibyte (KiB) is used instead.
A Kibibyte (KiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1024 bytes (or 8,192 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'kibi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'kilobyte' (KB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Megabit (Mb or Mbit) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1,000,000 bits and it is commonly used to express data transfer speeds, such as the speed of an internet connection and to measure the size of a file. In the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of mebibit (Mibit) is used instead.
A Mebibit (Mib or Mibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,048,576 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'mebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'megabit' (Mb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Megabyte (MB) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1,000,000 bytes (or 8,000,000 bits) and commonly used to express the size of a file or the amount of memory used by a program. It is also used to express data transfer speeds and in the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of mebibyte (MiB) is used instead.
A Mebibyte (MiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,048,576 bytes (or 8,388,608 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'mebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'megabyte' (MB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Gigabit (Gb or Gbit) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1,000,000,000 bits and it is commonly used to express data transfer speeds, such as the speed of an internet connection and to measure the size of a file. In the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of gibibit (Gibit) is used instead.
A Gibibit (Gib or Gibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,073,741,824 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'gibi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'gigabit' (Gb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Gigabyte (GB) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1,000,000,000 bytes (or 8,000,000,000 bits) and commonly used to measure the storage capacity of computer hard drives, flash drives, and other digital storage devices. It is also used to express data transfer speeds and in the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of Gibibyte (GiB) is used instead.
A Gibibyte (GiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,073,741,824 bytes (or 8,589,934,592 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'gibi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'gigabyte' (GB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Terabit (Tb or Tbit) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information transfer rate. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000 (one trillion) bits. It is commonly used to measure the speed of data transfer over computer networks, such as internet connection speeds.
A Tebibit (Tib or Tibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,099,511,627,776 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'tebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'terabit' (Tb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Terabyte (TB) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1,000,000,000,000 bytes (or 8,000,000,000,000 bits) and commonly used to measure the storage capacity of computer hard drives, flash drives, and other digital storage devices. It is also used to express data transfer speeds and in the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of Tebibyte (TiB) is used instead.
A Tebibyte (TiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,099,511,627,776 bytes (or 8,796,093,022,208 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'tebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'terabyte' (TB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Petabit (Pb or Pbit) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information transfer rate. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000 (one quadrillion) bits. It is commonly used to measure the speed of data transfer over computer networks, such as internet connection speeds.
A Pebibit (Pib or Pibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,125,899,906,842,624 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'pebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'petabit' (Pb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Petabyte (PB) is a decimal unit of digital information that is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000 bytes (or 8,000,000,000,000,000 bits) and commonly used to measure the storage capacity of enterprise storage arrays and data centers. It is also used to express data transfer speeds and in the context of data storage and memory, the binary-based unit of Pebibyte (PiB) is used instead.
A Pebibyte (PiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,125,899,906,842,624 bytes (or 9,007,199,254,740,992 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'pebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'petabyte' (PB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the storage size of high end servers and data storage arrays.
An Exabit (Eb or Ebit) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information transfer rate. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one quintillion) bits. It is used to measure the speed of extremely high-speed data transfer over communication networks, such as high-speed internet backbones and advanced computer networks.
An Exbibit (Eib or Eibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'exbi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'exabit' (Eb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
An Exabyte (EB) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information storage. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one quintillion) bytes, It is commonly used to measure the storage capacity of large data centers, computer hard drives, flash drives, and other digital storage devices.
An Exbibyte (EiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 bytes (or 9,223,372,036,854,775,808 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'exbi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'exabyte' (EB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the storage size of high end servers and data storage arrays.
A Zettabit (Zb or Zbit) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information transfer rate. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one sextillion) bits. It is used to measure the speed of extremely high-speed data transfer over communication networks, such as high-speed internet backbones and advanced computer networks. The zettabit is part of the International System of Units (SI) and the prefix zetta indicates multiplication by the seventh power of 1000.
A Zebibit (Zib or Zibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'zebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'zettabit' (Zb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Zettabyte (ZB) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information storage. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one sextillion) bytes. It is commonly used to measure the storage capacity of large data centers, computer hard drives, flash drives, and other digital storage devices.
A Zebibyte (ZiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,180,591,620,717,411,303,424 bytes (or 9,444,732,965,739,290,427,392 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'zebi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'zettabyte' (ZB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the storage size of high end servers and data storage arrays.
A Yottabit (Yb or Ybit) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information transfer rate. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one septillion) bits. It is used to measure the speed of extremely high-speed data transfer over communication networks, such as high-speed internet backbones and advanced computer networks.
A yobibit (Yib or Yibit) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 bits and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'yobi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'yottabit' (Yb). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the amount of data storage and data transfer in computer systems.
A Yottabyte (YB) is a decimal unit of measurement for digital information storage. It is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (one septillion) bytes. It is commonly used to measure the storage capacity of large data centers, computer hard drives, flash drives, and other digital storage devices.
A Yobibyte (YiB) is a binary unit of digital information that is equal to 1,208,925,819,614,629,174,706,176 bytes (or 9,671,406,556,917,033,397,649,408 bits) and is defined by the International Electro technical Commission(IEC). The prefix 'yibi' is derived from the binary number system and it is used to distinguish it from the decimal-based 'yottabyte' (YB). It is widely used in the field of computing as it more accurately represents the storage size of high end servers and data storage arrays.
 Data Unit Converter
Data Unit Converter